Distributed Tracing for Application Troubleshooting
Introduction
Distributed tracing is a method to track the flow and timing of application requests as they move through a system of components such as browsers, APIs, Databases and other infrastructure such as queues, data stores. The key idea is to link and trace requests across multiple services in a distributed architecture, which enables a comprehensive understanding of how a request progresses through various components, aiding in troubleshooting and optimizing the overall performance of the entire application stack.
How Distributed Tracing Works
There are mainly two components of tracing. Traces and spans. A trace represents the entire log of events that took place during a request, from initiation to completion. Each trace is composed of multiple spans. A span is a specific operation or task that contributes to the processing of a request, such as performing a database query or authentication. An initial request will create a root span. Root span, encapsulates the entire time taken for a request to be completed. If the initial request requires additional operations, the root span will create additional child spans, which can also create their own spans.
For example, consider an application that lets a user add tasks.
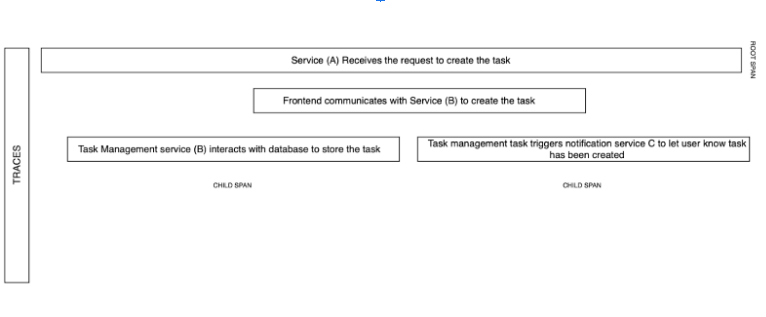
Conclusion
In the context of a task list application, this simplified example demonstrates how distributed tracing could be employed to visualize the user’s actions, such as adding and completing a task, as they traverse through different services. The trace context, including unique identifiers like trace and span IDs, helps correlate related spans, providing a comprehensive view of the end-to-end journey of a request. Distributed tracing is not only a powerful tool for troubleshooting and debugging but also a key component of observability in modern, complex systems. It allows development and operations teams to identify inefficiencies, optimize critical paths, and ensure a smooth and responsive user experience.
Platforms supporting Distributed Tracing functionality will be discussed in more detail in a subsequent blog.